What is cit0day? Understanding Data Breach Databases and Password Security
If you’ve stumbled upon the term “cit0day” while researching cybersecurity or data breaches, you’re probably wondering what it is and why it matters. Let me break it down for you in a way that’s actually useful.
What Exactly is cit0day?
cit0day (sometimes written as “cit zero day”) is essentially a search engine for leaked data. Think of it as Google, but instead of searching the web, it searches through massive databases of stolen information from data breaches.
Here’s the thing: when companies get hacked and user data gets stolen, that information doesn’t just disappear. It often ends up circulating in underground forums and databases. cit0day aggregates this leaked data, making it searchable.
What is cit0day Used For?
The platform serves different purposes depending on who’s using it:
Legitimate Security Research
- Security professionals use it to check if their organization’s data has been compromised
- Researchers analyze breach patterns and security vulnerabilities
- Individuals verify if their personal information has been leaked
The Dark Side
Unfortunately, cit0day is also used by malicious actors to:
- Find credentials for account takeover attacks
- Gather personal information for identity theft
- Launch targeted phishing campaigns
- Access password lists for credential stuffing attacks
Understanding Data Breaches and Password Dumps
Let me explain how this whole ecosystem works, because it’s actually pretty important to understand.
What Happens During a Data Breach?
When a company experiences a data breach, hackers typically gain access to:
- User credentials: Email addresses and passwords
- Personal information: Names, addresses, phone numbers
- Financial data: Sometimes credit card information
- Database dumps: Complete copies of user databases
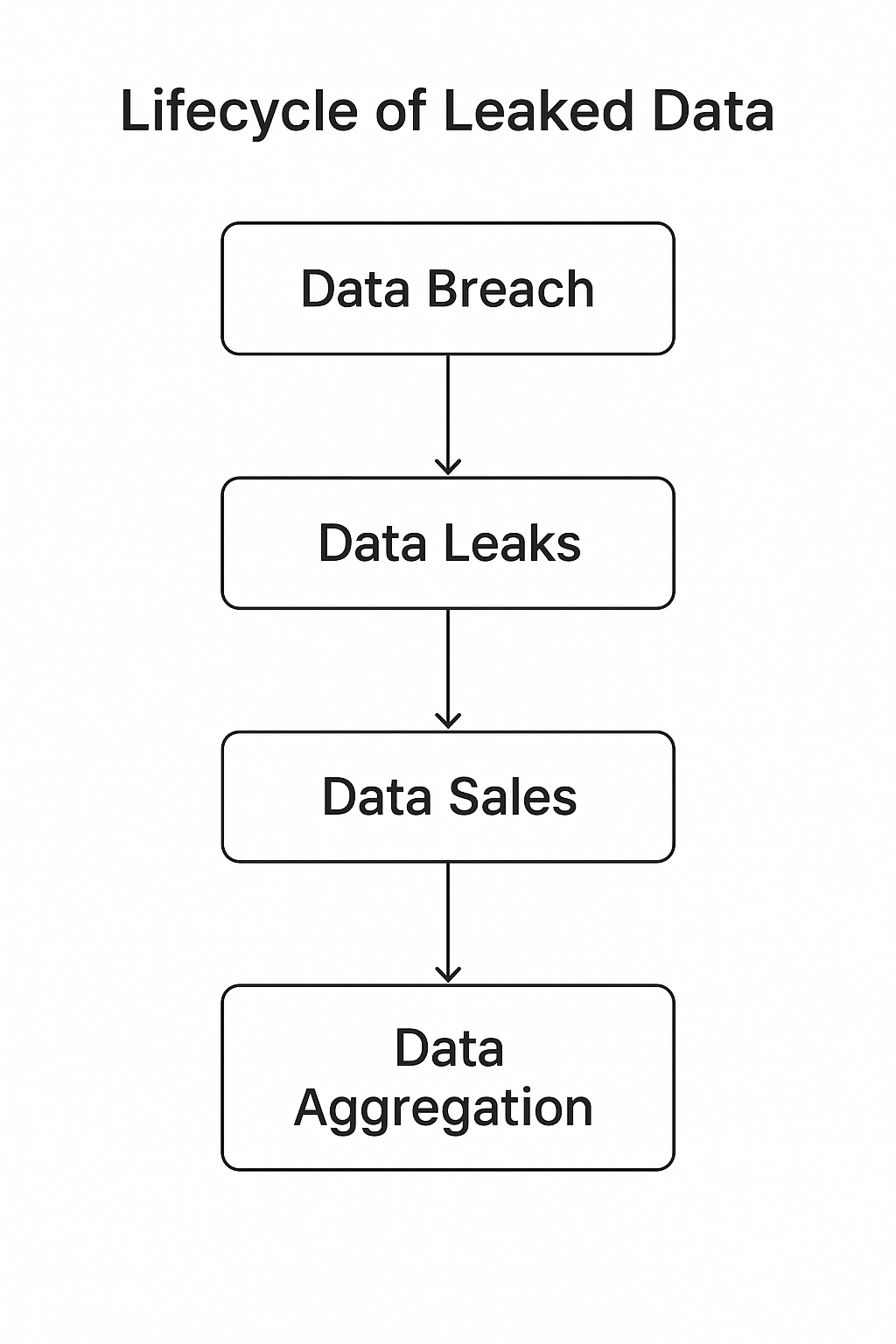
The Journey of Leaked Data
Here’s what typically happens after a breach:
- Initial Breach: Hackers compromise a company’s database
- Data Extraction: They download (dump) the entire database
- Underground Distribution: The data gets shared or sold on dark web forums
- Aggregation: Platforms like cit0day collect and index this data
- Searchability: The leaked information becomes easily searchable
The Real Danger: Password Reuse
Here’s where things get really concerning. The biggest risk isn’t just that your password from one site got leaked - it’s what happens next.
Credential Stuffing Attacks
Attackers use leaked password lists to try the same email/password combination across hundreds of different websites. So if you used the same password for:
- Your email account
- Your bank
- Your social media
- Your work accounts
One breach could compromise everything.
Real-World Example
Let’s say there was a breach at a small online forum you joined years ago. You used the password “Summer2020!” there. If you also used that same password for your email, attackers could:
- Find your credentials in the leaked database
- Try them on Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo
- Access your email
- Use password reset links to access your other accounts
- Potentially access your financial accounts
This isn’t theoretical - it happens thousands of times every day.
How to Check if You’ve Been Compromised
Before we talk about protection, you should know if your data is already out there:
Legitimate Checking Services
- Have I Been Pwned: The most trusted service (haveibeenpwned.com)
- Firefox Monitor: Mozilla’s breach checking tool
- Google Password Checkup: Built into Chrome
Important: Never enter your password into random “breach checking” websites. Legitimate services only need your email address.
Protecting Yourself: The Password Problem
So here’s the reality: most people know they should use strong, unique passwords for every account. But actually doing it? That’s where it gets tricky.
Why People Reuse Passwords
Let’s be honest about why this happens:
- Memory overload: You have dozens of accounts
- Convenience: It’s just easier to remember one password
- Complexity fatigue: Creating strong passwords is mentally exhausting
I get it. But here’s the thing - there’s actually a simple solution.
The Solution: Strong, Unique Passwords Made Easy
Instead of trying to remember complex passwords or writing them down, use a systematic approach:
Use Our Password Generator
Our Password Generator takes the headache out of creating secure passwords:
Key Features:
- Customizable strength: Choose length and character types
- Instant generation: Create passwords in seconds
- Multiple passwords: Generate several at once
- No storage: We don’t save or track your passwords
- Completely free: No registration required
How to Use It Effectively
Here’s my recommended workflow:
- Visit our Password Generator: Generate Password
- Set your requirements:
- Minimum 16 characters for important accounts
- Include uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Generate unique passwords for each account
- Store them securely in a password manager
[Image description: Screenshot of the password generator interface showing customization options]
Password Manager Integration
Generate your passwords with our tool, then store them in a password manager like:
- Bitwarden (open source and free)
- 1Password (user-friendly)
- LastPass (popular choice)
This way, you only need to remember one master password.
Database Downloads and Dumps: What You Need to Know
You might hear terms like “database dump” or “password list download” thrown around. Here’s what they mean:
Database Dumps
A database dump is essentially a complete copy of a database, usually in a format like:
- SQL files
- CSV exports
- JSON data
- Plain text lists
Why Dumps are Dangerous
These dumps often contain:
- Plaintext passwords: If the company didn’t hash passwords properly
- Hashed passwords: Which can sometimes be cracked
- Associated data: Email, username, personal info all linked together
The Scale of the Problem
Some major breaches have exposed:
- Yahoo: 3 billion accounts
- Facebook: 533 million users
- LinkedIn: 700 million users
- Adobe: 153 million accounts
That’s a lot of data floating around in these databases.
Practical Steps to Take Right Now
Okay, enough theory. Here’s what you should actually do:
Immediate Actions
- Check if you’ve been breached: Use Have I Been Pwned
- Change compromised passwords: Start with email and financial accounts
- Generate new passwords: Use our Password Generator
- Enable two-factor authentication: Everywhere that offers it
Long-term Security Habits
- Never reuse passwords: Each account gets a unique password
- Use a password manager: Let software remember for you
- Regular password updates: Change passwords for critical accounts annually
- Monitor your accounts: Check for suspicious activity
The Bigger Picture: Why This Matters
Here’s something that doesn’t get talked about enough: data breaches aren’t going away. In fact, they’re becoming more common.
The Reality Check
- Companies will continue to get breached
- Your data will likely be leaked at some point
- The question isn’t “if” but “when”
Your Best Defense
Since you can’t prevent companies from getting hacked, your best defense is:
- Unique passwords for every account
- Strong passwords that can’t be easily guessed
- Two-factor authentication as a second layer
This way, even if one account is compromised, the damage is contained.
Common Misconceptions
Let me clear up some myths I hear all the time:
Myth: “I’m not important enough to be targeted” Reality: Automated attacks don’t discriminate. They try every leaked credential everywhere.
Myth: “Complex passwords are enough” Reality: A complex password reused across sites is still vulnerable.
Myth: “I’ll remember unique passwords for each site” Reality: You won’t. Nobody can. That’s why password managers exist.
Why Our Password Generator is Different
There are lots of password generators out there, so why use ours?
Transparency
- No tracking: We don’t log what passwords you generate
- Client-side generation: Passwords are created in your browser
- No account required: Use it instantly, no signup
Flexibility
- Customizable options: Control every aspect of your password
- Bulk generation: Create multiple passwords at once
- Mobile-friendly: Works perfectly on phones and tablets
Integration-Ready
Generate passwords that work with any password manager or system. No proprietary formats or limitations.
Try it now: Password Generator
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it legal to access cit0day or similar databases? A: Accessing leaked data can be legally gray. Security professionals may use it for legitimate research, but downloading and using stolen credentials is illegal.
Q: How often should I change my passwords? A: For most accounts, changing passwords annually is sufficient if they’re strong and unique. Change immediately if you suspect a breach.
Q: Are password managers safe? A: Yes, reputable password managers use strong encryption. They’re much safer than reusing passwords or writing them down.
Q: What makes a password truly strong? A: Length (16+ characters), randomness, and uniqueness. Our generator creates passwords that meet all these criteria.
Q: Can I trust online password generators? A: Reputable ones like ours that generate passwords client-side (in your browser) are safe. Avoid generators that require sending data to a server.
Summary: Taking Control of Your Security
Here’s the bottom line: cit0day and similar databases exist because data breaches happen constantly. You can’t prevent companies from getting hacked, but you can control the damage.
The single most effective thing you can do is use strong, unique passwords for every account. And the easiest way to do that is with a good password generator.
Start protecting yourself today:
- Generate strong passwords with our Password Generator
- Store them in a password manager
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Check if you’ve been breached at Have I Been Pwned
Don’t wait until you’re the victim of account takeover. A few minutes now can save you hours of headache later.
Remember: in cybersecurity, the best defense is being proactive. And it all starts with better passwords.


